Facial Action Coding System (FACS)
Psychologically, FACS has redefined the study of nonverbal communication. It enables researchers to detect micro-expressions , brief, involuntary facial movements that reveal authentic emotions concealed behind social masks. These fleeting cues are often critical in clinical psychology, lie detection, behavioral therapy, and trauma research, helping psychologists recognize emotional incongruence or repressed affect. FACS decodes patterns like AU1 (inner brow raiser) and AU4 (brow lowerer) to indicate sadness or distress, while AU12 (lip corner puller) often signifies genuine happiness when paired with eye muscle activation. This level of granularity allows practitioners to assess emotional authenticity, empathy, and psychological defense mechanisms with high precision.
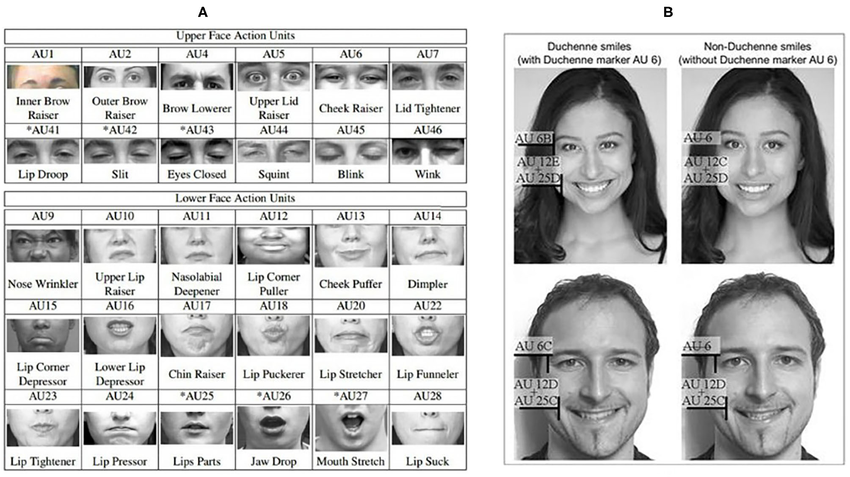
In Emotion AI , FACS is the backbone of facial emotion recognition systems . It trains AI to interpret the physical mechanics of facial movement, detecting changes in facial muscles, symmetry, and tension, to infer emotional states. When integrated with computer vision and deep learning , Emotion AI maps Action Units into emotional probabilities, allowing for subtle differentiation between emotions such as mild irritation versus intense anger, or polite smiles versus genuine joy. This transformation of visual input into emotional intelligence enables machines to interpret human emotion with remarkable accuracy.
Imentiv’s AI extends FACS-based facial analysis into a multimodal emotion recognition framework , combining visual, vocal , and textual emotion analysis. This layered approach allows Emotion AI to understand emotional patterns holistically, how facial cues correspond with tone of voice and linguistic emotion. For instance, FACS-driven facial analysis may identify micro-tension or suppressed sadness in user feedback, while audio emotion analysis detects voice tremors and text emotion analysis captures linguistic emotional tone. Together, these modalities generate comprehensive emotional insights that surpass what any single data stream could provide.
In applied settings, FACS-integrated Emotion AI supports diverse fields such as user experience research , advertising effectiveness studies , workplace well-being assessment, and virtual therapy. It enables organizations to identify emotional engagement, frustration, or stress levels during interactions, improving design empathy and communication strategies. In mental health and therapy contexts, FACS allows for emotion-informed monitoring, detecting subtle emotional fatigue, defensiveness, or progress over time, providing an additional layer of understanding that complements human intuition.
.png?alt=media&token=deb1c5eb-b30a-48a8-8d54-c5dab3eed813)
As Emotion AI continues to evolve, FACS remains a cornerstone of affective computing, ensuring that technological emotional recognition remains rooted in scientific accuracy, cross-cultural validity , and human behavioral authenticity . It represents the bridge between psychological theory and artificial emotional intelligence, translating the language of the human face into data that helps technology understand us better.
Discover How FACS Powers Emotion AI for Deeper Human Insight →