.jpg?alt=media&token=18892a58-97ca-4bf6-ad0e-8d1143ce4567?w=3840&q=75)
Leveraging Emotion AI for Better Business Development Webinars
Sales webinars are a key component of modern B2B sales and marketing strategies.
Webinars have evolved from mere information-sharing platforms to powerful tools for lead generation, customer engagement, and sales conversion. QuestionPro's webinar "More than words: Leveraging visuals to unlock emotionally rich qualitative insights", a prime example of a business development webinar, aimed to revolutionize how businesses approach qualitative research. By understanding user engagement through Imentiv AI (an emotion recognition technology), we can unlock valuable insights for optimizing webinar sales funnels.
This blog post will delve into the webinar's key takeaways and explore how Emotion AI can provide deeper insights into audience engagement, presenter impact, and overall sales webinar effectiveness.
Visual Storytelling: A Game-Changer for B2B Sales
The webinar, led by industry experts Jill Meneilley (QuestionPro Digsite Director) and Wayne and Susanna (Ah Ha), emphasized the transformative potential of visuals in qualitative research. By incorporating compelling visuals, businesses can create more engaging content foster deeper connections with audiences, and drive higher conversion rates. This aligns perfectly with the growing importance of visual storytelling in B2B sales and marketing.
Emotion AI: A New Lens for Webinar Analysis
While visual storytelling undoubtedly captivated audiences, Emotion AI takes audience analysis to a new level. Emotion AI can provide critical data points for refining your webinar sales funnel by identifying areas of high user engagement and interest by analyzing facial expressions, tone of voice, and body language.

Emotion AI Analysis of Webinar Video
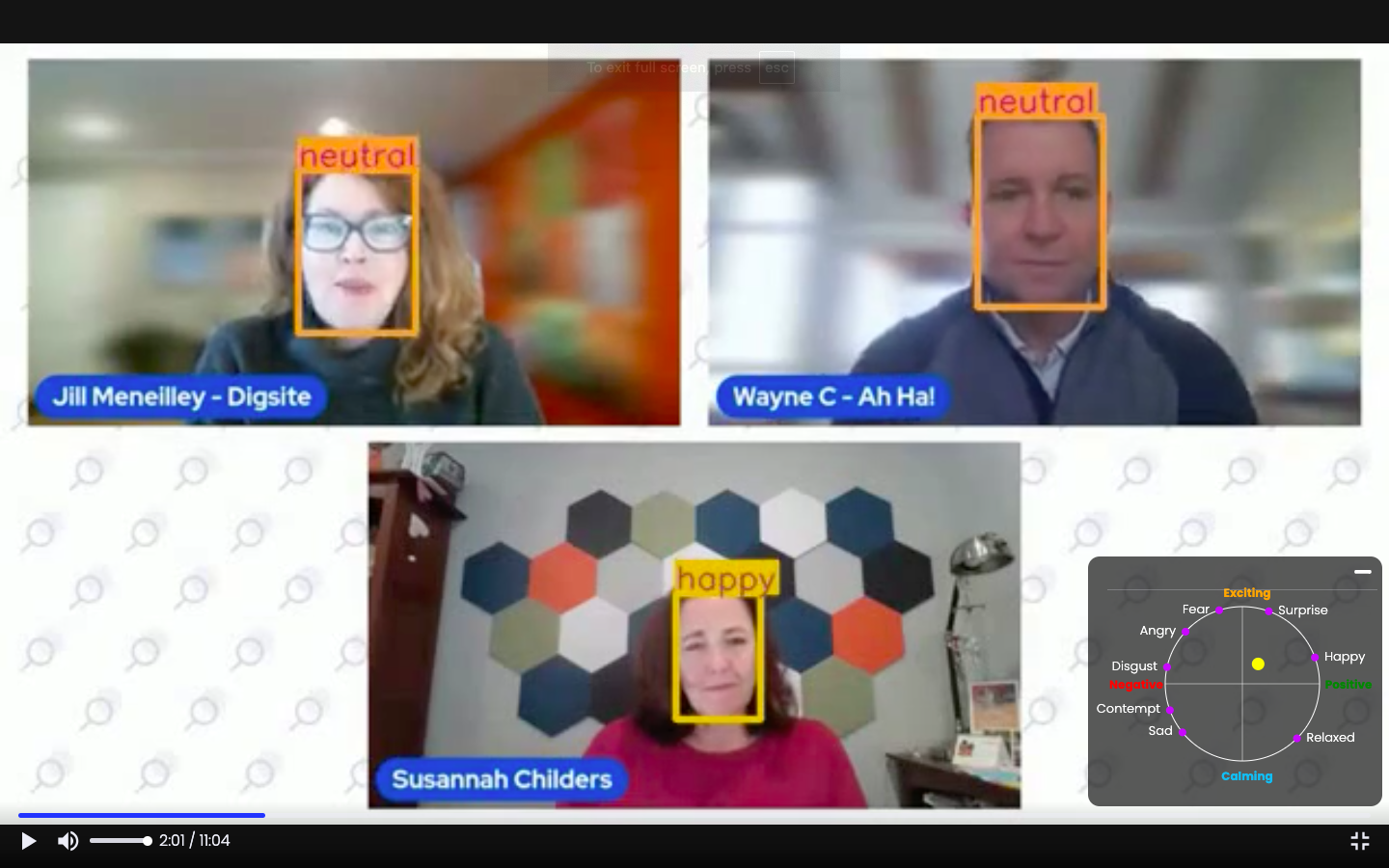
Let's break down the webinar analysis we conducted, using our Emotion AI software to understand the psychological and emotional dimensions captured in this sales webinar.
Facial Expressions and Emotions: Happy to Neutral (and Vice Versa)
In this webinar, the facial expressions and emotions of participants fluctuate between happy and neutral, reflecting an ongoing exchange of information that is both engaging and thoughtful.
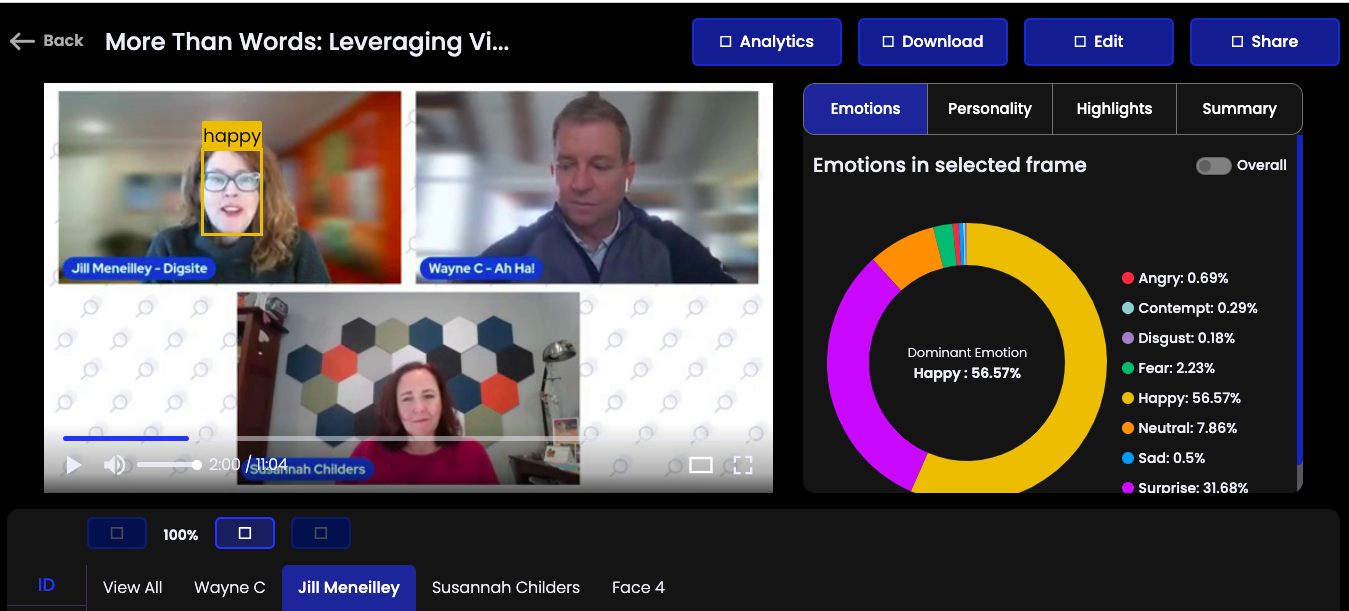
Happy Expressions
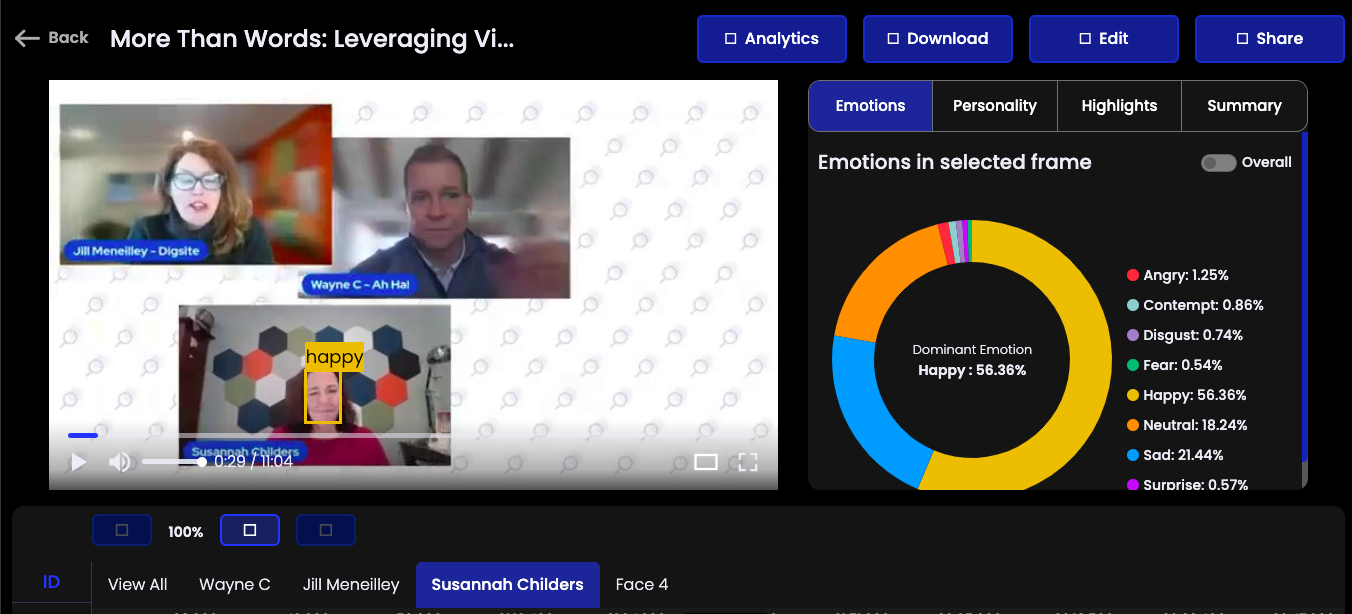
When participants display happy expressions, they often signal agreement, understanding, or appreciation of the content being discussed.
For example, when someone agrees with a point made during the webinar, they might smile, which is linked to the activation of the *zygomatic major muscle (*FACS Action Unit AU12), pulling the corners of the mouth upward. This can be further enhanced by AU6 (cheek raiser) and AU25 (lips part), which contribute to a genuine smile indicating happiness or interest.
These moments of happiness not only convey positive emotions but also encourage a collaborative atmosphere among participants.
Neutral Expressions
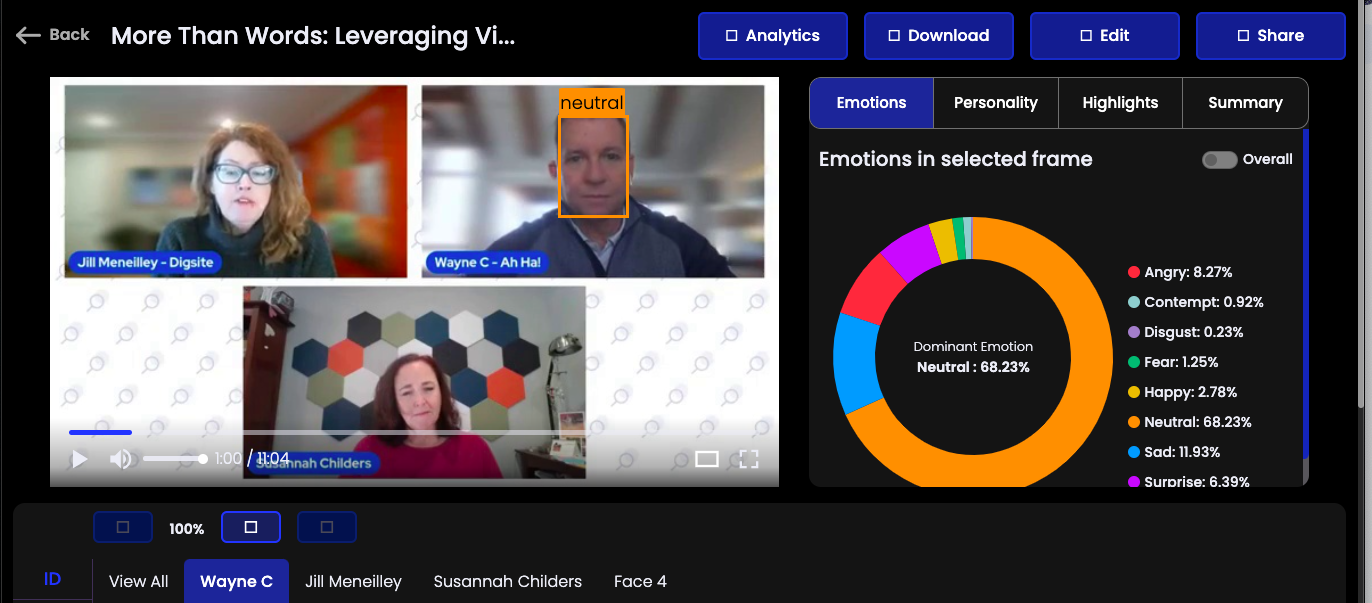
On the other hand, neutral expressions, characterized by relaxed facial muscles and minimal activation of emotional expression muscles like the zygomatic major (AU12), suggest that participants are focused on absorbing and processing the information being presented.
For instance, during a complex explanation, a participant might adopt a neutral expression as they concentrate on understanding the details. This neutrality indicates serious engagement and reflection, balancing the emotional tone of the webinar and showcasing the participants' thoughtful involvement in the discussion.
The shift between happy and neutral expressions reflects a dynamic balance between active engagement and thoughtful reflection, both of which are crucial aspects of the curiosity and desire for knowledge that define the epistemic emotion in the video.
Overall Video Emotion: Epistemic
The epistemic emotion, which is characterized by curiosity, inquiry, and a strong desire for knowledge, clearly dominates the overall tone of the webinar. This is not just a background feeling; it actively shapes the entire discussion. Participants consistently engage with the content in ways that reflect this emotion—they ask insightful questions, seek to explore new ideas, and respond thoughtfully to the information presented.
Their interactions throughout the webinar demonstrate a deep intellectual involvement and a shared eagerness to learn and understand the material being discussed. This pervasive sense of curiosity and inquiry drives the conversation and creates a dynamic, knowledge-focused atmosphere.
Curiosity and Exploration
Participants display curiosity through active engagement behaviors like nodding (associated with FACS AU1 - inner brow raiser) or slight head tilts, which signal attentiveness and interest in the content.
For example, during a new or surprising piece of information, you might notice participants nodding along or tilting their heads slightly as they process and explore the new concepts being discussed. This consistent shift from happy to neutral emotions reflects the cognitive process of learning and understanding, which are essential aspects of epistemic emotion.
Cognitive Engagement
The shifts between happy and neutral expressions also point to the participants' deep cognitive engagement. For instance, when someone smiles in recognition of a new insight or nods in agreement with the content, it shows that they are not only absorbing the information but also integrating it into their understanding.
This mental processing, a hallmark of epistemic emotion, underscores the intellectual engagement of the participants throughout the webinar.
Personality of the Video
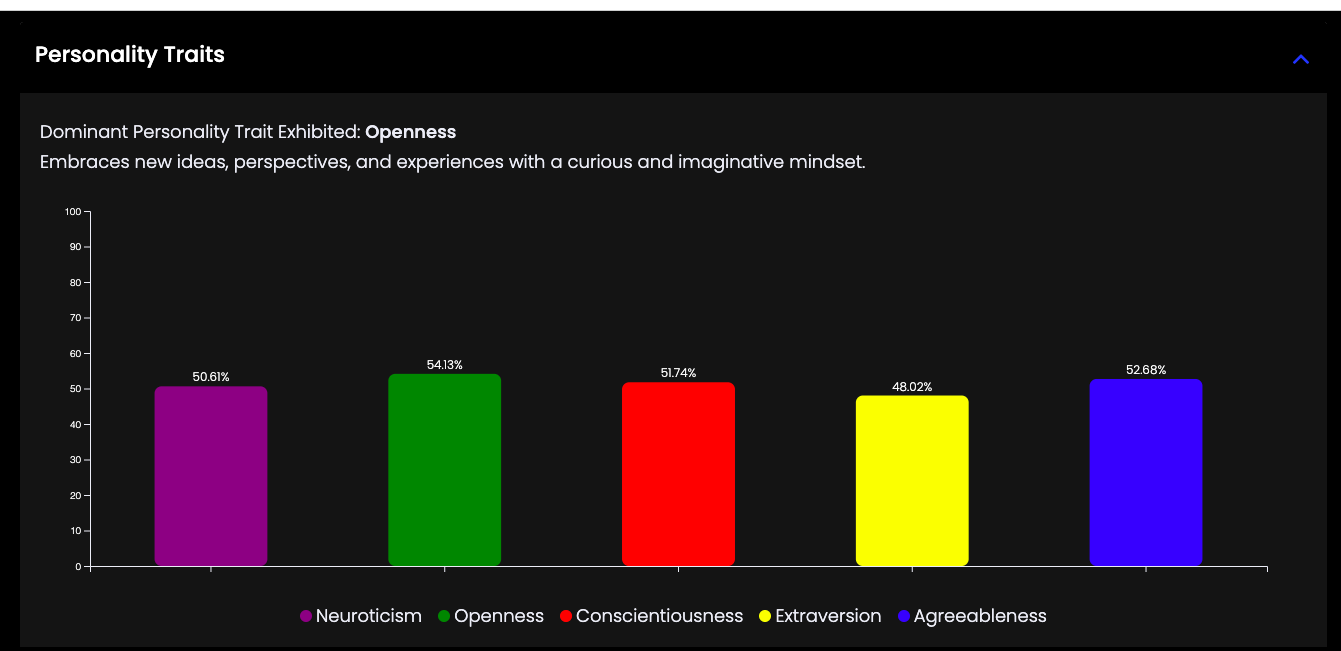
The webinar analysis with emotion recognition technology reveals that the predominant personality traits of the participants are openness and agreeableness.
Openness
The trait of openness is evident in the participants' willingness to consider new ideas and perspectives, as indicated by their facial expressions and body language. For example, the presence of relaxed expressions and occasional smiles suggests that participants are open to the information being presented.
Subtle cues, like the tightening of the eyelids (FACS AU7 - lid tightener) when participants are deeply concentrating, also indicate a blend of curiosity and openness to new concepts, further reinforcing this trait.
Agreeableness
Agreeableness is portrayed through frequent smiling (AU12), nodding, and other signs of positive social interaction. For instance, when participants smile or nod during the discussion, it reflects a supportive and friendly atmosphere where everyone’s contributions are valued.
The transitions from happy to neutral expressions also suggest a balance between assertiveness and empathy, both of which are key aspects of agreeableness and contribute to a harmonious and collaborative environment.
By understanding the nuances of user engagement through Emotion AI, as demonstrated in the QuestionPro webinar analysis, businesses can create more effective webinar sales funnels.
Leveraging Emotion AI for Enhanced Webinar Effectiveness

Emotion AI is a powerful tool for refining your webinar strategy. By identifying moments of high engagement and emotional connection, you can replicate these elements in future webinars.
Additionally, analyzing audience sentiment can help you tailor your content to specific audience segments.
Incorporating Emotion AI into your webinar analysis enables you to:
- Optimize content for maximum impact
- Improve presenter performance
- Enhance audience engagement
- Increase conversion rates
- Gain a competitive edge
By combining the qualitative insights from the webinar with quantitative data from Emotion AI, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of their audience, optimize content delivery, and improve overall webinar performance.
Our analysis provides valuable insights into the potential of Emotion AI in transforming webinar analytics. While this is just one example, the possibilities are vast. To explore more insights into sales webinar analysis, check out our blogs on Moveworks, Zendesk & Scale AI and Semrush.
Want to delve deeper into webinar analytics?
Glossary
Zygomatic Major Muscle: A facial muscle responsible for pulling the corners of the mouth upward, creating a smile. It is linked to positive emotions like happiness and is key to forming a genuine "Duchenne smile." Identified as Action Unit 12 (AU12) in facial coding.
FACS: The Facial Action Coding System, developed by Paul Ekman and Wallace V. Friesen, is a method for analyzing facial expressions by breaking them down into specific movements called Action Units (AUs).
AU (Action Unit): Fundamental components of FACS, each representing a specific facial muscle movement that helps decode emotions.
AU12 (Lip Corner Puller): Refers to the activation of the zygomatic major muscle, which lifts the corners of the mouth into a smile, indicating happiness or amusement.
AU6 (Cheek Raiser): Involves the contraction of the orbicularis oculi muscle, raising the cheeks and often creating crow’s feet, commonly seen in genuine smiles.
AU25 (Lips Part): Involves the parting of the lips, enhancing expressions like happiness or surprise and indicating readiness to communicate.
AU1 (Inner Brow Raiser): Refers to the upward movement of the inner eyebrows, associated with surprise, concern, or attentiveness, signaling emotional engagement.