Low Arousal
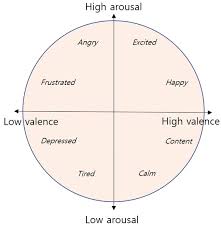
Low arousal refers to a physiological and emotional state marked by reduced activation, calmness, or subdued energy. It represents the lower end of the arousal spectrum, where the body and mind operate in a relaxed or passive mode rather than an alert or excited one. In emotional terms, low arousal corresponds to feelings such as calmness, serenity, contentment, or, in some cases, sadness and boredom, depending on the accompanying emotional valence. This state influences attention, motivation, and response speed, often facilitating reflection and recovery rather than action or stimulation.
.png?alt=media&token=5642f851-7097-46c4-b531-abd212557ee8)

Psychologically, low arousal plays a vital role in emotional regulation and well-being. It can foster tranquility, mindfulness, and cognitive clarity when experienced within a healthy range. However, prolonged low arousal, especially when paired with negative valence, can lead to disengagement, apathy, or depressive mood states. According to the
Valence-Arousal Model, emotions like relaxation (positive valence, low arousal) and sadness (negative valence, low arousal) exist in this zone, showing that not all low-energy states are undesirable, some are restorative, while others indicate emotional fatigue or detachment. Maintaining balance within the arousal spectrum helps individuals stay responsive without tipping into emotional underactivation or overstimulation.
In
Emotion AI analysis
, low arousal is identified as a decrease in physiological and expressive intensity across multimodal signals.
Imentiv AI
detects this through reduced
facial expressivity
(relaxed facial muscles, slower blinking),
vocal softness
(lower pitch, slower tempo, reduced amplitude), and
linguistic calmness
(neutral or minimal emotional language in text). During
video emotion recognition, low arousal periods may appear as subdued engagement or reflective moments within the viewer’s emotional timeline. By combining arousal intensity with valence direction, the system distinguishes between peaceful engagement (positive low arousal) and emotional withdrawal (negative low arousal).
From a technical standpoint, tracking low arousal helps Emotion AI detect
emotional stability, fatigue, or disengagement
, key insights in user experience research, wellness monitoring, and content optimization. For example, in workplace analytics, extended low-arousal states can indicate reduced motivation or burnout signals.
.png?alt=media&token=5642f851-7097-46c4-b531-abd212557ee8)
In product or media testing, consistent low-arousal responses may suggest that content lacks emotional
stimulation. By mapping these subtle variations, Emotion AI enhances interpretability of human affect, providing a more holistic view of emotional engagement across contexts.